
- Read past tense and past participle how to#
- Read past tense and past participle plus#
The present perfect tense expresses an action that began in the past and is now completed in the present.

Let’s start by talking about present perfect verbs. Verbs can appear in any one of three perfect tenses: present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect. In English, participles are also sometimes used to form compound words like “is going.” A past participle, in the context we’re using it today, is the second part of a compound verb that’s used to form perfect and passive tenses. Participles are words made out of verbs but used as adjectives. Past participle: read /red/ Present participle: reading /reeding/ Example sentences: She reads a lot.
Read past tense and past participle plus#
The perfect form is the verb tense used to talk about a completed action or condition and always uses a form of “have” or “had,” plus the past participle. The tense of a verb refers to the time of the action or state of being. Remember that verbs are words that describe an action, occurrence, or state of being.
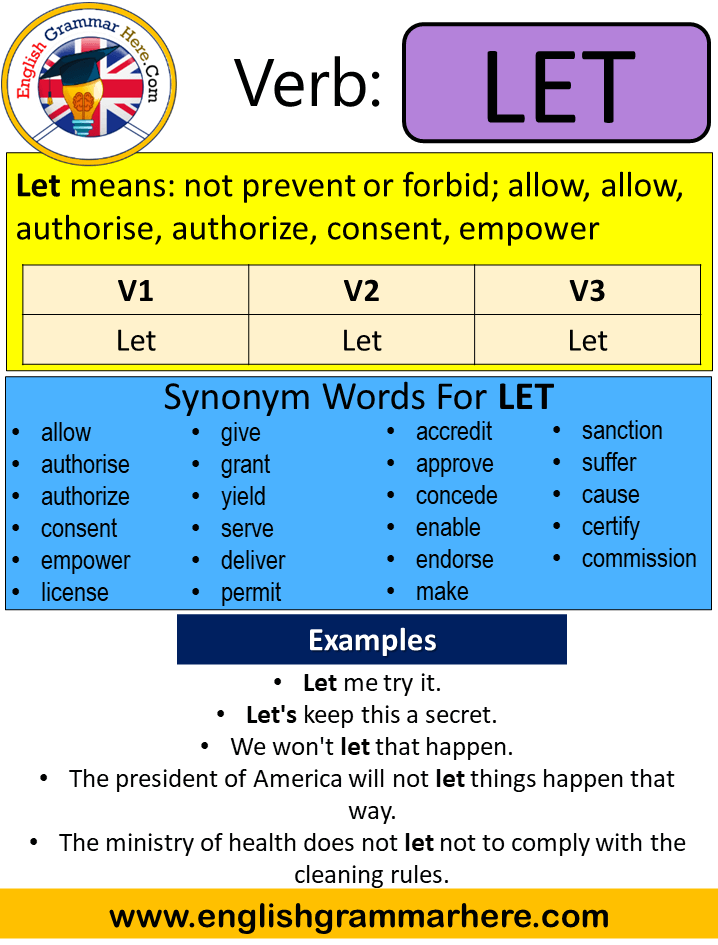
Irregular past participles do not follow a regular pattern and have a range of word endings, not just “-ed.” And while some irregular verbs use the same form for the simple past tense and past participle (e.g., bend/ bent/ bent), others use different forms (e.g., drive/ drove/ driven).Today we’re going to be talking about the difference between present perfect, past perfect, and future perfect verb tenses.
 Regular past participles are all formed by adding “-ed,” “-ied,” or “-d” and match the simple past tense form of the verb (e.g., the simple past tense and past participle forms of “kick” are both “kicked”). When forming a past participle, it will usually end “-ed.” You can see this in most of the examples above! But this depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular. In the first sentence above, the linking verb “were” connects the noun “kids” and the past participle “bored.” And in the second, we link “boy” (noun) and “excited” (past participle) with the verb “seems.” Regular vs. However, we can also use past participles as modifiers after a linking verb, such as in the following: Here, the past participles “shocked” and “broken” modify the nouns “look” and “watch,” respectively. She took her broken watch to get repaired. He couldn’t hide the shocked look on his face. Typically, this involves placing the past participle before the word we want to modify, such as in the following sentences: What Is the Past Participle of 'Read' Time for a bonus round The past participle is not actually a tense. We can also use past participles as adjectives (i.e., to modify a noun or pronoun). But these use present participles instead (i.e., verbs that end “-ing,” like “looking”). There are also continuous perfect tenses, such as the present perfect continuous, which are concerned with ongoing actions. He will have finished his homework by tomorrow morning. If we had looked harder, we would have found it.Īnd the future perfect is for actions that will be complete by a certain time: She had danced there several times before. The past perfect, meanwhile, is used for actions completed before a point in time (either specified or unspecified) or a conditional set in the past: She has walked to work four times this week so far. We use the present perfect tense for things that began in the past and remain true or to discuss actions completed within a stated ongoing time: Future perfect = will have + past participle (e.g., I will have looked). Past perfect = had + past participle (e.g., I had looked). Present perfect = have/has + past participle (e.g., I have looked). The Perfect TensesĪs verbs, we use past participles to express a completed action in the perfect tenses (i.e., the present, past, and future perfect tenses): And after that, to finish the post, we’ll look at the difference between regular and irregular past participles. As an adjective to modify a noun or pronoun. To form the perfect tenses (e.g., present perfect, past perfect). Past participles are a type of verb used in two main situations:
Regular past participles are all formed by adding “-ed,” “-ied,” or “-d” and match the simple past tense form of the verb (e.g., the simple past tense and past participle forms of “kick” are both “kicked”). When forming a past participle, it will usually end “-ed.” You can see this in most of the examples above! But this depends on whether the verb is regular or irregular. In the first sentence above, the linking verb “were” connects the noun “kids” and the past participle “bored.” And in the second, we link “boy” (noun) and “excited” (past participle) with the verb “seems.” Regular vs. However, we can also use past participles as modifiers after a linking verb, such as in the following: Here, the past participles “shocked” and “broken” modify the nouns “look” and “watch,” respectively. She took her broken watch to get repaired. He couldn’t hide the shocked look on his face. Typically, this involves placing the past participle before the word we want to modify, such as in the following sentences: What Is the Past Participle of 'Read' Time for a bonus round The past participle is not actually a tense. We can also use past participles as adjectives (i.e., to modify a noun or pronoun). But these use present participles instead (i.e., verbs that end “-ing,” like “looking”). There are also continuous perfect tenses, such as the present perfect continuous, which are concerned with ongoing actions. He will have finished his homework by tomorrow morning. If we had looked harder, we would have found it.Īnd the future perfect is for actions that will be complete by a certain time: She had danced there several times before. The past perfect, meanwhile, is used for actions completed before a point in time (either specified or unspecified) or a conditional set in the past: She has walked to work four times this week so far. We use the present perfect tense for things that began in the past and remain true or to discuss actions completed within a stated ongoing time: Future perfect = will have + past participle (e.g., I will have looked). Past perfect = had + past participle (e.g., I had looked). Present perfect = have/has + past participle (e.g., I have looked). The Perfect TensesĪs verbs, we use past participles to express a completed action in the perfect tenses (i.e., the present, past, and future perfect tenses): And after that, to finish the post, we’ll look at the difference between regular and irregular past participles. As an adjective to modify a noun or pronoun. To form the perfect tenses (e.g., present perfect, past perfect). Past participles are a type of verb used in two main situations: 
Read past tense and past participle how to#
But what exactly is a past participle? And how do past participles work? In this post, we’ll explain the basics of how to use these words in your writing. You almost certainly use past participles on a daily basis if you speak English.








 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
